# Bean
在IoC容器内,这些bean定义表示为org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition对象,这些对象包含(除其他信息外)以下元数据:
| Property | Explained in… |
|---|---|
| Class | Instantiating Beans (opens new window) |
| Name | Naming Beans (opens new window) |
| Scope | Bean Scopes (opens new window) |
| Constructor arguments | Dependency Injection (opens new window) |
| Properties | Dependency Injection (opens new window) |
| Autowiring mode | Autowiring Collaborators (opens new window) |
| Lazy initialization mode | Lazy-initialized Beans (opens new window) |
| Initialization method | Initialization Callbacks (opens new window) |
| Destruction method | Destruction Callbacks (opens new window) |
# Bean 作用域
| Scope | 描述 |
|---|---|
| singleton | (默认)一个IoC容器只会对一个bean定义一个实例(单例模式 (opens new window))。 |
| prototype | 每次请求bean时IoC容器都会创建一个新的实例(多例模式)。 |
| request | Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a single HTTP request. That is, each HTTP request has its own instance of a bean created off the back of a single bean definition. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext. |
| session | Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of an HTTP Session. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext. |
| application | Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a ServletContext. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext. |
| websocket | Scopes a single bean definition to the lifecycle of a WebSocket. Only valid in the context of a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext. |
# 单例bean源码分析
注册/获取一个单例的bean
// org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java
public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
@Override
public void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) throws IllegalStateException {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
Assert.notNull(singletonObject, "Singleton object must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object oldObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (oldObject != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not register object [" + singletonObject +
"] under bean name '" + beanName + "': there is already object [" + oldObject + "] bound");
}
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
/**
* Add the given singleton object to the singleton cache of this factory.
* <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonObject the singleton object
*/
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
return getSingleton(beanName, true);
}
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name.
* <p>Checks already instantiated singletons and also allows for an early
* reference to a currently created singleton (resolving a circular reference).
* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for
* @param allowEarlyReference whether early references should be created or not
* @return the registered singleton object, or {@code null} if none found
*/
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
Spring 中的单例 bean 是否有线程安全问题?
存在线程安全问题。因为,当多个线程操作同一个对象的时候,对这个对象的成员变量的写操作会存在线程安全问题。
但是,一般情况下,我们常用的Controller、Service、Dao这些Bean是无状态的。无状态的Bean不能保存数据,因此是线程安全的。
常见的有2种解决办法:
- 在类中定义一个
ThreadLocal成员变量,将需要的可变成员变量保存在ThreadLocal中(推荐的一种方式)。 - 改变
Bean的作用域为“prototype”:每次请求都会创建一个新的bean实例,自然不会存在线程安全问题。
# Bean 生命周期
图示:
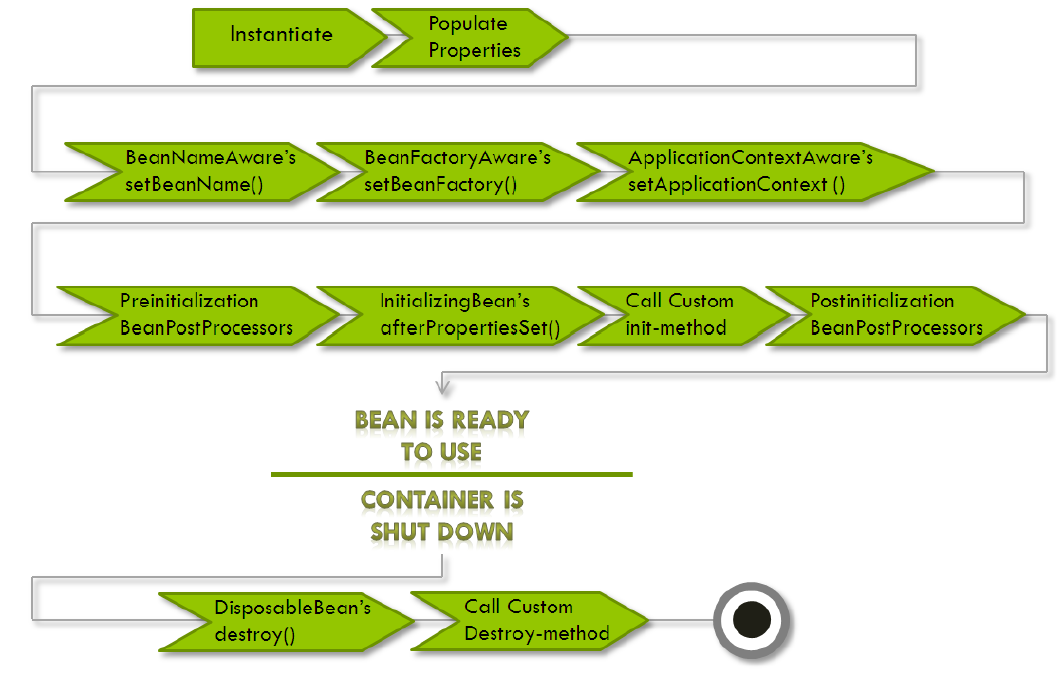
- 创建一个Bean的实例,使用构造器实例化。
- 如果涉及到一些属性值,则利用
setXXX()方法注入属性。 - 如果Bean 实现了
BeanNameAware接口,调用setBeanName()方法,传入Bean的名字。 - 如果Bean 实现了
BeanClassLoaderAware接口,调用setBeanClassLoader()方法,传入ClassLoader对象的实例。 - 与上面的类似,如果实现了其他 *.Aware接口,就调用相应的方法。
- 如果有和这个Bean的Spring容器相关的
BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法。 - 如果Bean实现了
InitializingBean接口,执行afterPropertiesSet()方法。 - 如果Bean定义包含
init-method属性,执行指定的方法。 - 如果有和这个Bean的Spring容器相关的
BeanPostProcessor对象,执行postProcessAfterInitialization()方法。 - 当要销毁Bean的时候,如果Bean实现了
DisposableBean接口,执行destroy()方法。 - 当要销毁Bean的时候,如果Bean定义包含
destroy-method属性,执行指定的方法。
# 定义类并实现 *.Aware 接口、InitializingBean 接口
/**
* 实现Bean的生命周期接口,四个接口,要实现其中的四个方法,实例化和初始化完成后会自动被调用
*
* @author : zhangquansheng
* @date : 2020/9/1 13:18
*/
@Slf4j
public class SmsBean implements BeanNameAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
private String content;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private String beanName;
public SmsBean() {
log.info("【构造器】调用SmsBean的构造器实例化");
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
log.info("【注入属性】注入属性content={}", content);
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
log.info("【BeanFactoryAware接口】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()");
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
log.info("【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName(), beanName={}", name);
this.beanName = name;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//同一级的生命周期方法中最后一个被调用的,但是只会调用一次,之后在调用bean的setxx()方法更改属性时将不会再被被调用到
log.info("【InitializingBean接口】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
log.info("【ApplicationContextAware】调用setApplicationContext()");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
log.info("【DisposableBean接口】调用DisposableBean.destroy()");
}
public void myInit() {
log.info("【init-method】调用<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法");
}
public void myDestroy() {
log.info("【destroy-method】调用<bean>destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法");
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
log.info("【BeanClassLoaderAware】调用setBeanClassLoader()");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
# 创建一个 Bean 的实例,使用构造器实例化。
/**
* BeanConfig
*
* @author : zhangquansheng
* @date : 2020/9/1 17:09
*/
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "myInit", destroyMethod = "myDestroy")
public SmsBean sms() {
SmsBean sms = new SmsBean();
sms.setContent("007");
return sms;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# BeanPostProcessor(Bean 后置处理器)
作用
BeanPostProcessor是Spring IOC容器提供的一个扩展接口,通过BeanPostProcessor对Spring管理的bean进行再加工,比如可以修改bean的属性等。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof SmsBean) {
log.info("调用postProcessBeforeInitialization() 对{}进行加工", beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof SmsBean) {
log.info("调用postProcessAfterInitialization() 再次获得{}加工机会", beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
控制台打印如下:
SmsBean.java:25 - 【构造器】调用SmsBean的构造器实例化
SmsBean.java:33 - 【注入属性】注入属性content=007
SmsBean.java:45 - 【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName(), beanName=sms
SmsBean.java:75 - 【BeanClassLoaderAware】调用setBeanClassLoader()
SmsBean.java:39 - 【BeanFactoryAware接口】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()
SmsBean.java:57 - 【ApplicationContextAware】调用setApplicationContext()
MyBeanPostProcessor.java:21 - 调用postProcessBeforeInitialization() 对sms进行加工
SmsBean.java:52 - 【InitializingBean接口】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()
SmsBean.java:66 - 【init-method】调用<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法
MyBeanPostProcessor.java:31 - 调用postProcessAfterInitialization() 再次获得sms加工机会
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
延伸思考
Spring项目启动非常的慢,为了定位问题,我们如何打印出每个Bean加载到Ioc容器的时间呢?
实现BeanPostProcessor接口,通过Map记录postProcessBeforeInitialization的加载时间,然后在postProcessAfterInitialization处理打印出Bean加载时间。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* LoggerBeanLoadCostPostProcessor
*
* @author quansheng1.zhang
* @since 2020/12/26 17:22
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class LoggerBeanLoadCostPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private static Map<String, Long> cost = new HashMap<>(10000);
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
log.info("first load-spring-bean-cost-info, bean init beanName:{}, begin time : {}", beanName, System.currentTimeMillis());
cost.put(beanName, System.currentTimeMillis());
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (cost.get(beanName) == null) {
log.warn("first load-spring-bean-cost-info, cost.get(beanName : {} ) is null", beanName);
} else {
log.info("first load-spring-bean-cost-info, bean after beanName:{}, beanType :{} before: {}, cost : {}ms", beanName, bean.getClass().getName(), cost.get(beanName), (System.currentTimeMillis() - cost.get(beanName)));
}
return bean;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# InitializingBean 和 DisposableBean 接口
bean实现InitializingBean和DisposableBean接口是为了让Spring容器对bean的生命周期进行管理,Spring容器可以在afterPropertiesSet()和destroy()方法中执行某些操作。
特别提示
在JSR-250中, @PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注释被认为是Spring应用程序中接收生命周期回调的最佳实践。使用这些注释意味着bean不耦合到Spring特定的接口。有关详细信息,请参见使用 @PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy (opens new window)。
如果你不希望使用JSR-250注解,并且希望bean不耦合到Spring特定的接口中,考虑使用init-method和destroy-method。
# 初始化回调
org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean容器在bean上设置了所有必需的属性后,该接口可让bean执行初始化工作。
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
2
3
4
5
我们建议您不要使用InitializingBean接口,因为它将代码与Spring耦合。
# 销毁回调
org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean当包含该接口的容器被销毁时,实现该接口可使Bean获得回调。建议使用@PostConstruct注释或者在bean上使用init method属性
public interface DisposableBean {
void destroy() throws Exception;
}
2
3
4
5
我们建议您不要使用DisposableBean回调接口,因为它不必要地将代码与Spring耦合。建议使用@PreDestroy注释或者在bean上使用destroy method属性
# FactoryBean
一般情况下,Spring通过反射机制利用bean的class属性指定实现类实例化Bean,在某些情况下,实例化Bean过程比较复杂,如果按照传统的方式,则需要在bean中提供大量的配置信息。配置方式的灵活性是受限的,这时采用编码的方式可能会得到一个简单的方案。
Spring为此提供了一个org.springframework.bean.factory.FactoryBean的工厂类接口,用户可以通过实现该接口定制实例化Bean的逻辑。FactoryBean接口对于Spring框架来说占用重要的地位,Spring自身就提供了50多个FactoryBean的实现。
它们隐藏了实例化一些复杂Bean的细节,给上层应用带来了便利。从Spring3.0开始,FactoryBean开始支持泛型,即接口声明改为FactoryBean<T>的形式。
源码如下:
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
@Nullable
T getObject() throws Exception;
@Nullable
Class<?> getObjectType();
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
FactoryBean 接口提供了三种方法:
Object getObject():返回由FactoryBean创建的Bean实例,如果isSingleton()返回true,则该实例会放到Spring容器中单实例缓存池中;boolean isSingleton():返回由FactoryBean创建的Bean实例的作用域是singleton还是prototype;Class getObjectType():返回FactoryBean创建的Bean类型。
总结一下 FactoryBean 和 BeanFactory 的区别?
其实它们仅仅类名比较类似而已,实际上BeanFactory是一个IOC容器(对象工厂),提供了最简单的容器的功能;而FactoryBean是工厂类接口,用户可以通过实现该接口定制实例化Bean的逻辑。
← IoC Spring 循环依赖 🎉 →
